Radio Properties of WISE-Selected AGN in ASKAP-EMU
Kelsey Hargraves
Supervisor: Dr. Michael Cowley
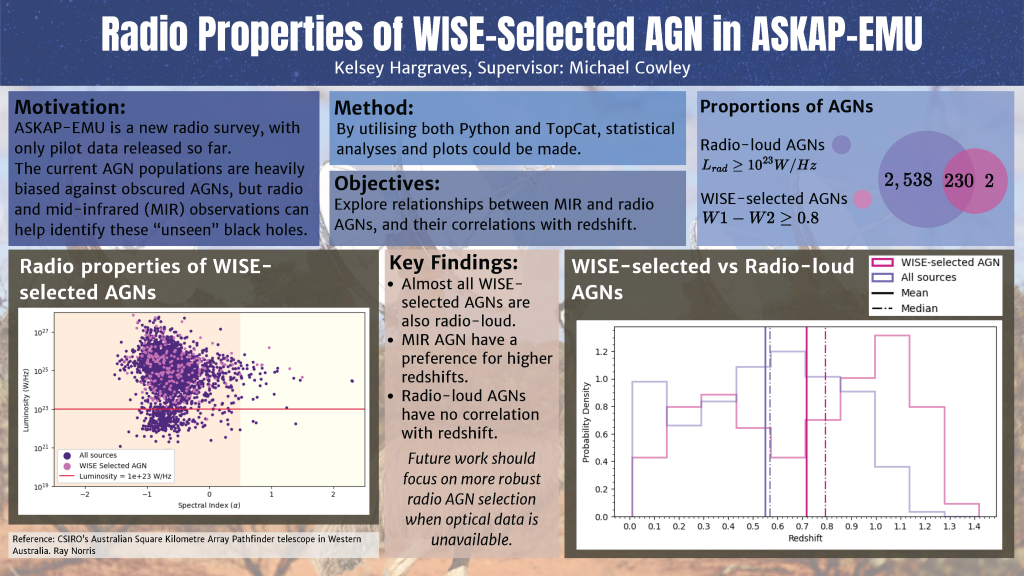
Active galactic nuclei (AGNs) play a critical role in understanding galaxy evolution and the history of the universe, however current methods of selecting AGNs from galaxies are biased towards optically bright sources. This work utilises the pilot data from the ASKAP-EMU survey, a radio survey centred at 944 MHz, as well as data from the CatWISE survey, which features the mid-infrared bands W1 (3.4μm) and W2 (4.6μm). The WISE surveys have been increasingly used to select mid-infrared AGNs using different colour cuts of W1−W2; a colour cut of W1 −W2 ≥ 0.8 was used in this project which correlates with a completeness of 78%. The selection of radio AGNs was based on the Lradio > 1023W/Hz criteria. This research aims to explore the correlations between radio and infrared AGNs and delve into the relationship between these properties and their redshifts. By cross-matching the ASKAP-EMU and CatWISE surveys in-depth statistical analyses were undertaken to investigate the AGNs properties. The findings show that 99% of the WISE-selected AGNs are also radio-loud; however, only 8% of radio-loud AGNs are also WISE-selected. We also found a binomial distribution of WISE-selected AGNs against redshift that is not present in the radio-loud AGN population, as well as a preference for higher redshifts for the mid-infrared AGNs. The differences between radio AGN and mid-infrared AGN highlight the importance of multi-wavelength analysis of AGNs, which helps us understand both the evolution of individual black holes and of AGN populations throughout cosmic time.
Media Attributions
- Radio properties of WISE-Selected AGN in ASKAP-EMU © Kelsey Hargraves is licensed under a CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial) license